The solar system is a fascinating and complex realm that has captured the imagination of scientists, astronomers, and the general public for centuries. It is our cosmic neighborhood, containing a variety of celestial bodies and phenomena that play a crucial role in the universe’s dynamics. This article will explore the components of the solar system, its formation, and its significance, shedding light on the mysteries of our planetary home.
What Is the Solar System?
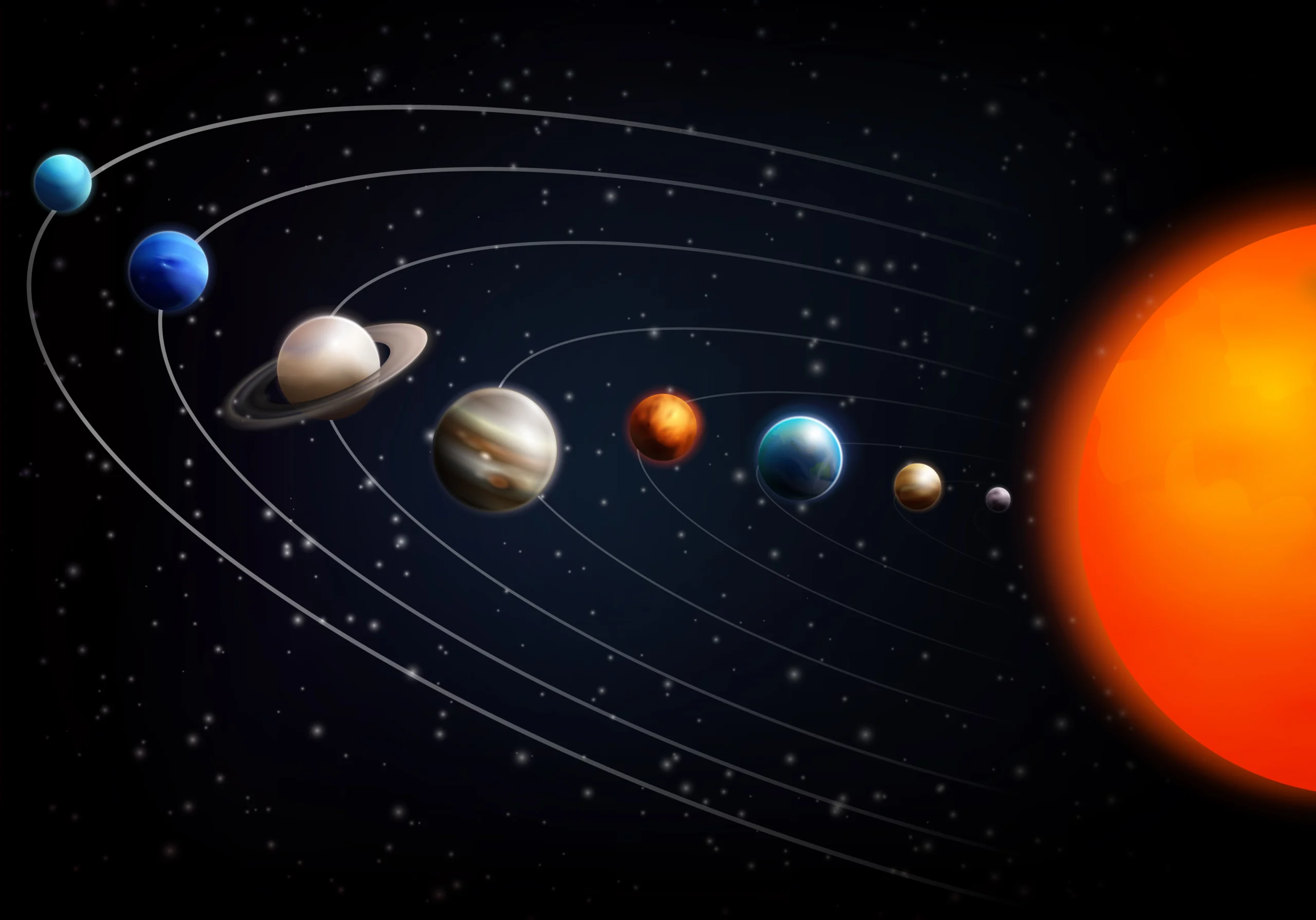
The solar system is a collection of celestial objects that are bound by gravity to a central star, the Sun. It consists of eight major planets, their moons, dwarf planets, comets, asteroids, and meteoroids. Together, these components create a dynamic environment that has fascinated humanity since ancient times.
Read Also :- What is Graphic Design?
Components of the Solar System
- The Sun
- The Sun is the heart of the solar system and is classified as a G-type main-sequence star (G dwarf). It accounts for about 99.86% of the solar system’s total mass, providing the light and heat necessary for life on Earth.
- The Planets
- The solar system contains eight major planets, divided into two categories: terrestrial (rocky) and gas giants. Terrestrial Planets
- Mercury: The closest planet to the Sun, Mercury is small, rocky, and lacks a substantial atmosphere.
- Venus: Known for its thick, toxic atmosphere, Venus has surface temperatures hot enough to melt lead.
- Earth: The only planet known to support life, Earth has abundant water and a diverse climate.
- Mars: Often referred to as the “Red Planet,” Mars is known for its iron oxide-rich surface and potential signs of past life. Gas Giants
- Jupiter: The largest planet in the solar system, Jupiter has a thick atmosphere and is known for its Great Red Spot, a massive storm.
- Saturn: Famous for its stunning ring system, Saturn is a gas giant with numerous moons.
- Uranus: An ice giant with a unique tilt, Uranus rotates on its side, leading to extreme seasonal changes.
- Neptune: The farthest planet from the Sun, Neptune is known for its deep blue color and strong winds.
- Dwarf Planets
- Dwarf planets are celestial bodies that orbit the Sun and have similar characteristics to planets but do not clear their orbital paths. Notable examples include Pluto, Eris, and Ceres.
- Moons
- Many planets have natural satellites, known as moons. Earth has one moon, while Jupiter has over 79 confirmed moons, including Ganymede, the largest moon in the solar system.
- Asteroids and Comets
- The asteroid belt, located between Mars and Jupiter, contains millions of rocky bodies. Comets, composed of ice and dust, originate from the Kuiper Belt and the Oort Cloud, often exhibiting spectacular tails when they approach the Sun.
Must Read :- What is HTML?
Formation of the Solar System
The solar system formed approximately 4.6 billion years ago from a giant molecular cloud. Here’s a brief overview of the process:
- Nebula Stage
- The solar nebula, a rotating cloud of gas and dust, began to collapse under its gravity. This collapse led to the formation of the Sun at the center.
- Protoplanetary Disk
- As the nebula spun faster, it flattened into a disk. The particles within the disk began to collide and stick together, forming larger bodies called planetesimals.
- Planet Formation
- These planetesimals continued to collide, eventually forming protoplanets. Some of these grew large enough to become the planets we know today.
- Clearing the Orbit
- The gravitational interactions among these newly formed planets cleared their orbits of smaller debris, leading to the arrangement we observe now.
Read More :- What is GDP?
The Importance of the Solar System
The solar system is not just a collection of celestial bodies; it holds immense significance for scientific research, technological advancements, and our understanding of the universe.
Scientific Exploration
Understanding the solar system provides insights into the formation of planetary systems, the potential for life beyond Earth, and the history of our own planet. Missions such as NASA’s Mars Rover and the Voyager spacecraft have expanded our knowledge of planetary atmospheres, geology, and potential habitability.
Technological Advancements
The study of the solar system has driven technological innovation. Satellite technology, GPS systems, and advances in materials science have all emerged from space exploration efforts.
Educational Impact
The solar system serves as a gateway for educating the public about science and space. Planetariums, science centers, and educational programs engage people of all ages, fostering a sense of curiosity and wonder about the universe.
Conclusion
The solar system is a captivating and intricate system that plays a vital role in the universe. Composed of the Sun, eight planets, moons, dwarf planets, asteroids, and comets, it offers a glimpse into the dynamic processes that govern celestial bodies. Understanding the solar system enhances our knowledge of planetary formation, technological advancements, and the potential for life beyond Earth. As we continue to explore our cosmic neighborhood, we uncover new mysteries and deepen our appreciation for the vastness of space.
In summary, the solar system is not just our home; it is a rich field of study that holds the keys to understanding the cosmos and our place within it.