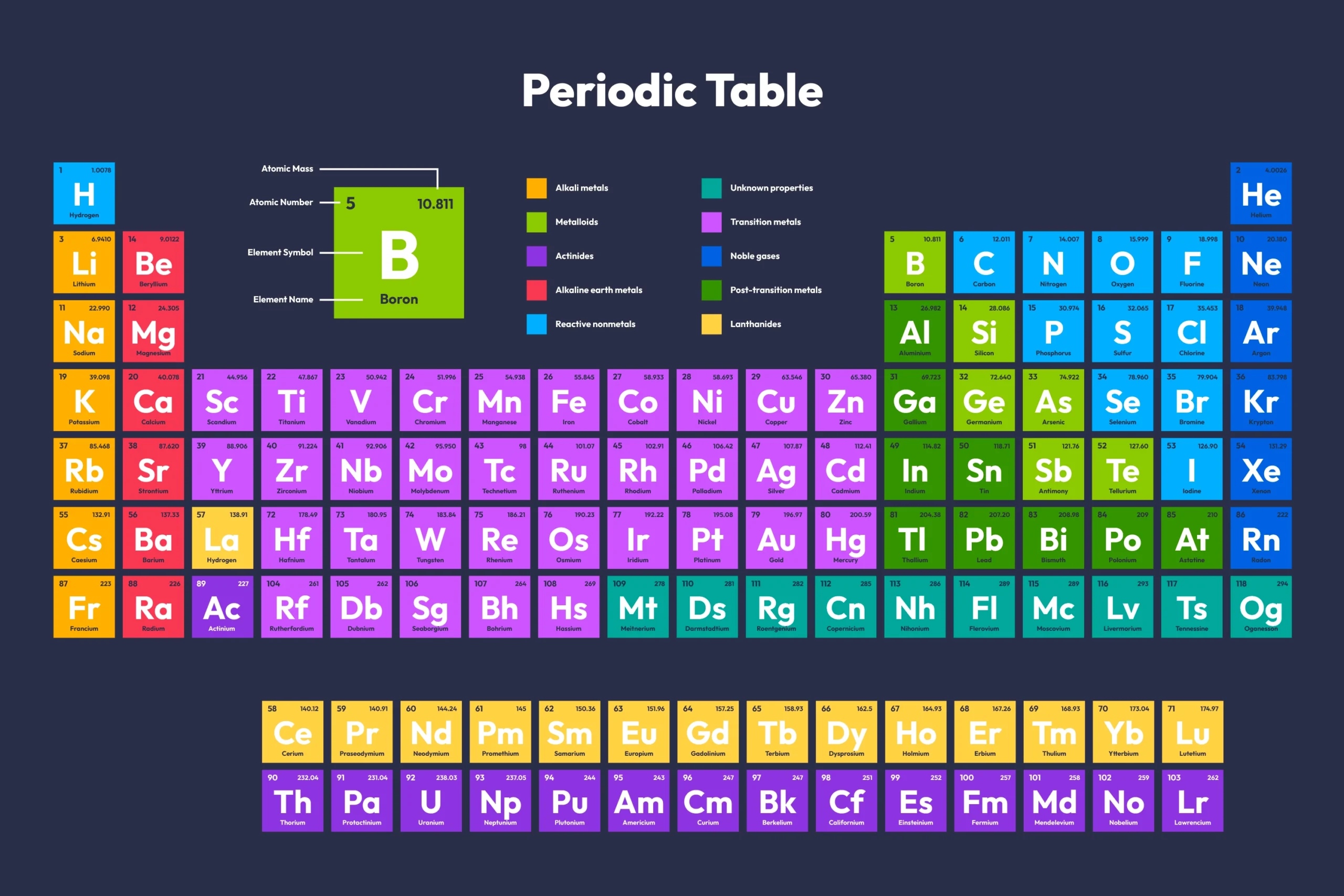
The periodic table of elements is a cornerstone of chemistry and science at large. It organizes all known chemical elements in a systematic manner, highlighting their relationships and properties. This fundamental tool is not only crucial for understanding the basic building blocks of matter but also serves as a guide for scientific discovery and technological advancement. This article delves into the significance of the periodic table, exploring its history, structure, and impact on science and industry.
Understanding the Periodic Table
What is the Periodic Table?
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organized by increasing atomic number and grouped by similar properties. Each element is represented by its chemical symbol, atomic number, and atomic mass. The table is divided into periods (rows) and groups (columns), reflecting periodic trends in element properties.
The Structure of the Periodic Table
- Periods: The horizontal rows in the periodic table are called periods. Elements within the same period have the same number of electron shells.
- Groups: The vertical columns are known as groups or families. Elements in the same group share similar chemical properties due to having the same number of electrons in their outer shell.
Historical Background
Early Discoveries and Development
The concept of the periodic table dates back to the early 19th century. Early chemists began organizing elements based on their properties and atomic masses. Key milestones include:
- Johann Döbereiner (1829): Döbereiner proposed the Law of Triads, which suggested that elements with similar properties occurred in groups of three.
- Alexandre de Chancourtois (1862): Chancourtois created the first version of the periodic table, known as the “Telluric Helix,” which arranged elements based on their atomic masses.
Dmitri Mendeleev and the Modern Periodic Table
The modern periodic table is credited to Dmitri Mendeleev, who in 1869 published a table that organized elements by increasing atomic mass and grouped them based on chemical properties. Mendeleev’s table successfully predicted the existence and properties of elements that were yet to be discovered, a testament to its accuracy and utility.
The Importance of the Periodic Table
Organizing Chemical Information
The periodic table serves as an essential tool for organizing and summarizing chemical information. By arranging elements in a structured manner, it provides a clear and concise overview of element properties and relationships.
Predicting Element Properties
The periodic table allows scientists to predict the properties of elements based on their position in the table. For example:
- Reactivity: Elements in the same group often exhibit similar reactivity. For instance, alkali metals (Group 1) are highly reactive with water.
- Electronegativity: Trends in electronegativity (the ability of an atom to attract electrons) can be observed across periods and groups, influencing chemical bonding and reactions.
Identifying Trends and Patterns
The periodic table highlights periodic trends and patterns, such as atomic radius, ionization energy, and electron affinity. These trends are crucial for understanding how elements interact and form compounds.
Facilitating Chemical Research and Innovation
Guiding Chemical Synthesis
The periodic table guides chemists in synthesizing new compounds and materials. By understanding the properties and reactivity of elements, scientists can design and create novel substances with specific characteristics.
Advancing Material Science
The periodic table plays a vital role in material science, where the properties of elements and their compounds are explored to develop advanced materials. For example, the discovery of new alloys and semiconductors relies on understanding the periodic trends of elements.
Applications in Various Fields
Medicine
The periodic table’s elements are fundamental to medicine. Elements such as iodine, iron, and platinum are used in diagnostics, treatment, and drug development. For example:
- Iodine: Used as a contrast agent in imaging techniques.
- Iron: Essential for blood formation and used in supplements.
- Platinum: Utilized in chemotherapy drugs like cisplatin.
Industry
The periodic table also impacts various industrial processes. Elements and compounds are used in manufacturing, energy production, and environmental management. Examples include:
- Catalysts: Elements like platinum and palladium are used in catalytic converters to reduce vehicle emissions.
- Batteries: Lithium, cobalt, and nickel are crucial in rechargeable batteries for electronic devices.
The Periodic Table and Education
Teaching Chemistry
The periodic table is a fundamental educational tool in chemistry. It helps students and educators understand the relationships between elements and their properties. The table’s organization aids in teaching concepts such as:
- Atomic Structure: The table illustrates how electrons are arranged in shells around the nucleus.
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding how elements bond based on their position in the table.
Inspiring Future Scientists
The periodic table inspires curiosity and exploration in the field of chemistry. By studying the table, students and researchers can uncover new elements and compounds, contributing to scientific knowledge and technological progress.
The Evolution of the Periodic Table
Discovery of New Elements
Since Mendeleev’s time, the periodic table has evolved with the discovery of new elements. The addition of elements beyond uranium, known as transuranium elements, has expanded the table. These elements are synthesized in laboratories and have applications in various scientific fields.
Advancements in Table Design
The periodic table has also seen advancements in its design and representation. Various formats, such as the long form and the modern layout with f-block elements, provide different perspectives on element organization and properties.
Conclusion
The periodic table is more than just a chart of elements; it is a profound representation of the building blocks of matter and the relationships between them. Its significance extends beyond the classroom and laboratory, impacting various fields from medicine to industry and inspiring scientific discovery and innovation. As our understanding of elements continues to grow and new discoveries are made, the periodic table will remain a vital tool in exploring the wonders of the chemical world and advancing human knowledge. Its enduring legacy reflects the ingenuity and curiosity that drive scientific progress and the quest to unravel the mysteries of the universe.